Python 之 OpenGL程序环境
发布时间:2019-09-09 08:48:40编辑:auto阅读(2838)
Python+OpenGL,想想都觉得很刺激~~
首先还是下载PyOpenGL包:http://pypi.python.org/pypi/PyOpenGL/3.0.2
在windows下,安装还是很简单的,安装程序会主动找到你的python目录,所以可以直接下一步。
安装好了后,就来写一个脚本测试一下~
test.py
from OpenGL.GL import *
from OpenGL.GLU import *
from OpenGL.GLUT import *
def Draw():
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT)
glRotatef(0.5, 0, 1, 0)
glutWireTeapot(0.5)
glFlush()
glutInit()
glutInitDisplayMode(GLUT_SINGLE | GLUT_RGBA)
glutInitWindowSize(400, 400)
glutCreateWindow("test")
glutDisplayFunc(Draw)
glutIdleFunc(Draw)
glutMainLoop()
可以看到,在python中同样可以使用glut来创建窗口,语法遵从Python,但是大体上的结构还是和c语言的glut库差不多。
在OpenGL织梦之旅【第二章】第2节.实现动画这篇博文中,我用c语言,用OpenGL实现了一个显示时钟的程序。和上面的脚本一样,那个程序也使用了glut库,那是不是意味着用Python也能够实现同样的东西呢?
答案当然是!
于是,我抱着好奇的心态去尝试了一下。最后居然成功了。。
有图有真相:
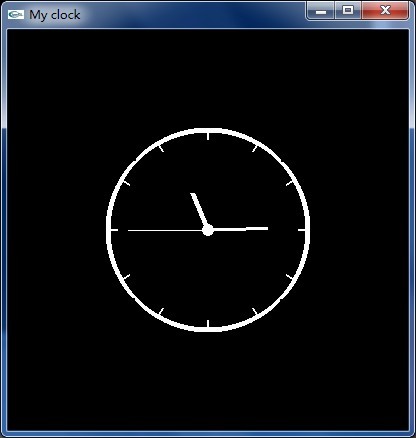
在转换的时候,有很多注意事项:
1.全局变量的处理。在Update函数和Draw函数中会用到h,m,s三个表示时间的全局变量。在Update函数中给他们更新值的时候需要用global关键字来声明一下。
2.三角函数。记得import math,调用的时候也要用math.cos和math.sin。
3.变量的数据类型。因为Python中不需要事先声明变量类型,所以有些值在赋值时需要注意,如果是浮点实数,但值需要暂时赋为一个整数时,需要在后面加上.0。如count=60.0
4.缩进的问题。在Python中代码段是用缩进来标示的。在c语言的OpenGL中,我习惯性地把glBegin(XXX)后定点的语句缩进一下,但是这个在Python中是会出现问题的。
最后附上代码:
from OpenGL.GL import *
from OpenGL.GLU import *
from OpenGL.GLUT import *
import math
import time
h=0
m=0
s=0
def Draw():
PI=3.1415926
R=0.5
TR=R-0.05
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT)
glLineWidth(5)
glBegin(GL_LINE_LOOP)
for i in range(100):
glVertex2f(R*math.cos(2*PI/100*i),R*math.sin(2*PI/100*i))
glEnd()
glLineWidth(2)
for i in range(100):
glBegin(GL_LINES)
glVertex2f(TR*math.sin(2*PI/12*i),TR*math.cos(2*PI/12*i))
glVertex2f(R*math.sin(2*PI/12*i),R*math.cos(2*PI/12*i))
glEnd()
glLineWidth(1)
h_Length=0.2
m_Length=0.3
s_Length=0.4
count=60.0
s_Angle=s/count
count*=60
m_Angle=(m*60+s)/count
count*=12
h_Angle=(h*60*60+m*60+s)/count
glLineWidth(1)
glBegin(GL_LINES)
glVertex2f(0.0,0.0)
glVertex2f(s_Length*math.sin(2*PI*s_Angle),s_Length*math.cos(2*PI*s_Angle))
glEnd()
glLineWidth(5)
glBegin(GL_LINES)
glVertex2f(0.0,0.0)
glVertex2f(h_Length*math.sin(2*PI*h_Angle),h_Length*math.cos(2*PI*h_Angle))
glEnd()
glLineWidth(3)
glBegin(GL_LINES)
glVertex2f(0.0,0.0)
glVertex2f(m_Length*math.sin(2*PI*m_Angle),m_Length*math.cos(2*PI*m_Angle))
glEnd()
glLineWidth(1)
glBegin(GL_POLYGON)
for i in range(100):
glVertex2f(0.03*math.cos(2*PI/100*i),0.03*math.sin(2*PI/100*i));
glEnd()
glFlush()
def Update():
global h,m,s
t=time.localtime(time.time())
h=int(time.strftime('%H',t))
m=int(time.strftime('%M',t))
s=int(time.strftime('%S',t))
glutPostRedisplay()
glutInit()
glutInitDisplayMode(GLUT_SINGLE | GLUT_RGBA)
glutInitWindowSize(400, 400)
glutCreateWindow("My clock")
glutDisplayFunc(Draw)
glutIdleFunc(Update)
glutMainLoop()
上一篇: Python GUI 之 Combobo
下一篇: python进阶用法3 【优化毫不起眼的
- openvpn linux客户端使用
51929
- H3C基本命令大全
51699
- openvpn windows客户端使用
42018
- H3C IRF原理及 配置
38857
- Python exit()函数
33345
- openvpn mac客户端使用
30315
- python全系列官方中文文档
28954
- python 获取网卡实时流量
23969
- 1.常用turtle功能函数
23885
- python 获取Linux和Windows硬件信息
22251
- Ubuntu本地部署dots.ocr
377°
- Python搭建一个RAG系统(分片/检索/召回/重排序/生成)
2588°
- Browser-use:智能浏览器自动化(Web-Agent)
3260°
- 使用 LangChain 实现本地 Agent
2712°
- 使用 LangChain 构建本地 RAG 应用
2700°
- 使用LLaMA-Factory微调大模型的function calling能力
3427°
- 复现一个简单Agent系统
2656°
- LLaMA Factory-Lora微调实现声控语音多轮问答对话-1
3494°
- LLaMA Factory微调后的模型合并导出和部署-4
5759°
- LLaMA Factory微调模型的各种参数怎么设置-3
5536°
- 姓名:Run
- 职业:谜
- 邮箱:383697894@qq.com
- 定位:上海 · 松江
