复现一个简单Agent系统
发布时间:2025-08-12 10:03:36编辑:Run阅读(2978)
大模型的能力是毋庸置疑的,但大模型在一些实时的问题上,或是某些专有领域的问题上,可能会显得有些力不从心。因此,需要一些工具来为大模型赋能,给大模型一个抓手,让大模型和现实世界发生的事情对齐颗粒度,这样就获得了一个更好的用的大模型。
这里基于React的方式,制作了一个最小的Agent结构(其实更多的是调用工具)一步一步手写Agent,可以让我们对Agent的构成和运作更加的了解。
实现细节
第一步:构造大模型
首先需要一个大模型,这里使用internlm2_5-7b-chat-1m作为Agent 模型。
InternLM2.5 是一个针对实际场景定制的聊天模型。该模型具有以下特点:
卓越的推理能力:在数学推理方面表现出色,超越了 Llama3 和 Gemma2-9B 等模型。
1M 上下文窗口:在 1M 长上下文中几乎完美地找到关键信息,在长上下文任务(如 LongBench)上表现领先。可以通过 LMDeploy 尝试 1M 上下文推理,并查看 文件聊天示例。
更强的工具使用能力:InternLM2.5 支持从超过 100 个网页中收集信息,相关实现将在 Lagent 中发布。InternLM2.5 在指令遵循、工具选择和反思方面有更好的工具利用能力。可以使用transformers库来加载InternLM2模型。
下载模型:
git clone https://www.modelscope.cn/Shanghai_AI_Laboratory/internlm2_5-7b-chat-1m.git
首先,先创建一个BaseModel类,可以在这个类中定义一些基本的方法,比如chat方法和load_model方法,方便以后扩展使用其他模型。
接着,创建一个InternLM2类,这个类继承自BaseModel类,在这个类中实现chat方法和load_model方法。就和正常加载InternLM2模型一样,来做一个简单的加载和返回即可。
创建llm.py文件
代码如下:
from typing import Dict, List, Optional, Tuple, Union
import torch
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM
class BaseModel:
def __init__(self, path: str = '') -> None:
self.path = path
def chat(self, prompt: str, history: List[dict]):
pass
def load_model(self):
pass
class InternLM2Chat(BaseModel):
def __init__(self, path: str = '') -> None:
super().__init__(path)
self.load_model()
def load_model(self):
print('================ Loading model ================')
self.tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(self.path, trust_remote_code=True)
self.model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(self.path, torch_dtype=torch.float16, trust_remote_code=True).cuda().eval()
print('================ Model loaded ================')
def chat(self, prompt: str, history: List[dict], meta_instruction:str ='') -> str:
response, history = self.model.chat(self.tokenizer, prompt, history, temperature=0.1, meta_instruction=meta_instruction)
return response, history
if __name__ == '__main__':
model = InternLM2Chat('/home/sam_admin/my_agent/models/internlm2_5-7b-chat-1m')
print(model.chat('你好', []))运行python llm.py,如下:

第二步: 构造工具在tools.py文件中,构造一些工具,比如Google搜索。在这个文件中,构造一个Tools类。在这个类中,需要添加一些
工具的描述信息和具体实现方式。
添加工具描述信息,是为了在构造system_prompt的时候,让模型能够知道可以调用哪些工具,以及工具描述信息和参数。
首先要在 tools 中添加工具的描述信息;
然后在 tools 中添加工具的具体实现;
使用Google搜索功能的话需要去serper官网申请一下token: https://serper.dev/dashboard, 然后在tools.py文件中
填写你的key,这个key每人可以免费申请一个,且有2500次的免费调用额度,足够做实验用啦~
创建tool.py文件
代码如下:
import os, json
import requests
"""
工具函数
- 首先要在 tools 中添加工具的描述信息
- 然后在 tools 中添加工具的具体实现
- https://serper.dev/dashboard
"""
class Tools:
def __init__(self) -> None:
self.toolConfig = self._tools()
def _tools(self):
tools = [
{
'name_for_human': '谷歌搜索',
'name_for_model': 'google_search',
'description_for_model': '谷歌搜索是一个通用搜索引擎,可用于访问互联网、查询百科知识、了解时事新闻等。',
'parameters': [
{
'name': 'search_query',
'description': '搜索关键词或短语',
'required': True,
'schema': {'type': 'string'},
}
],
}
]
return tools
def google_search(self, search_query: str):
url = "https://google.serper.dev/search"
payload = json.dumps({"q": search_query})
headers = {
'X-API-KEY': 'google搜索API_KEY',
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
}
response = requests.request("POST", url, headers=headers, data=payload).json()
return response['organic'][0]['snippet']
if __name__ == "__main__":
search_query = '今天关于AI的最新消息'
tools = Tools()
msg = tools.google_search(search_query)
print(msg)运行tool.py,如下:

第三步: 构造Agent
在Agent.py文件中,构造一个Agent类,这个Agent是一个React范式的Agent,在这个Agent类中,
实现了text_completion方法,这个方法是一个对话方法,在这个方法中,调用InternLM2模型,然后根据React的Agent
的逻辑,来调用Tools中的工具。
首先要构造system_prompt, 这个是系统的提示,可以在这个提示中,添加一些系统的提示信息,比如ReAct形式的prompt。
创建agent.py文件
代码如下:
from typing import Dict, List, Optional, Tuple, Union
import json5
from llm import InternLM2Chat
from tool import Tools
TOOL_DESC = """{name_for_model}: Call this tool to interact with the {name_for_human} API. What is the {name_for_human} API useful for? {description_for_model} Parameters: {parameters} Format the arguments as a JSON object."""
REACT_PROMPT = """尽你所能回答以下问题。可以使用以下工具:
{tool_descs}
Use the following format:
Question: the input question you must answer
Thought: you should always think about what to do
Action: the action to take, should be one of [{tool_names}]
Action Input: the input to the action
Observation: the result of the action
... (this Thought/Action/Action Input/Observation can be repeated zero or more times)
Thought: I now know the final answer
Final Answer: the final answer to the original input question
Begin!
"""
class Agent:
def __init__(self, path: str = '') -> None:
self.path = path
self.tool = Tools()
self.system_prompt = self.build_system_input()
self.model = InternLM2Chat(path)
def build_system_input(self):
tool_descs, tool_names = [], []
for tool in self.tool.toolConfig:
tool_descs.append(TOOL_DESC.format(**tool))
tool_names.append(tool['name_for_model'])
tool_descs = '\n\n'.join(tool_descs)
tool_names = ','.join(tool_names)
sys_prompt = REACT_PROMPT.format(tool_descs=tool_descs, tool_names=tool_names)
return sys_prompt
def parse_latest_plugin_call(self, text):
plugin_name, plugin_args = '', ''
i = text.rfind('\nAction:')
j = text.rfind('\nAction Input:')
k = text.rfind('\nObservation:')
if 0 <= i < j: # If the text has `Action` and `Action input`,
if k < j: # but does not contain `Observation`,
text = text.rstrip() + '\nObservation:' # Add it back.
k = text.rfind('\nObservation:')
plugin_name = text[i + len('\nAction:') : j].strip()
plugin_args = text[j + len('\nAction Input:') : k].strip()
text = text[:k]
return plugin_name, plugin_args, text
def call_plugin(self, plugin_name, plugin_args):
plugin_args = json5.loads(plugin_args)
if plugin_name == 'google_search':
return '\nObservation:' + self.tool.google_search(**plugin_args)
def text_completion(self, text, history=[]):
text = "\nQuestion:" + text
response, his = self.model.chat(text, history, self.system_prompt)
print(response)
plugin_name, plugin_args, response = self.parse_latest_plugin_call(response)
if plugin_name:
response += self.call_plugin(plugin_name, plugin_args)
response, his = self.model.chat(response, history, self.system_prompt)
return response, his
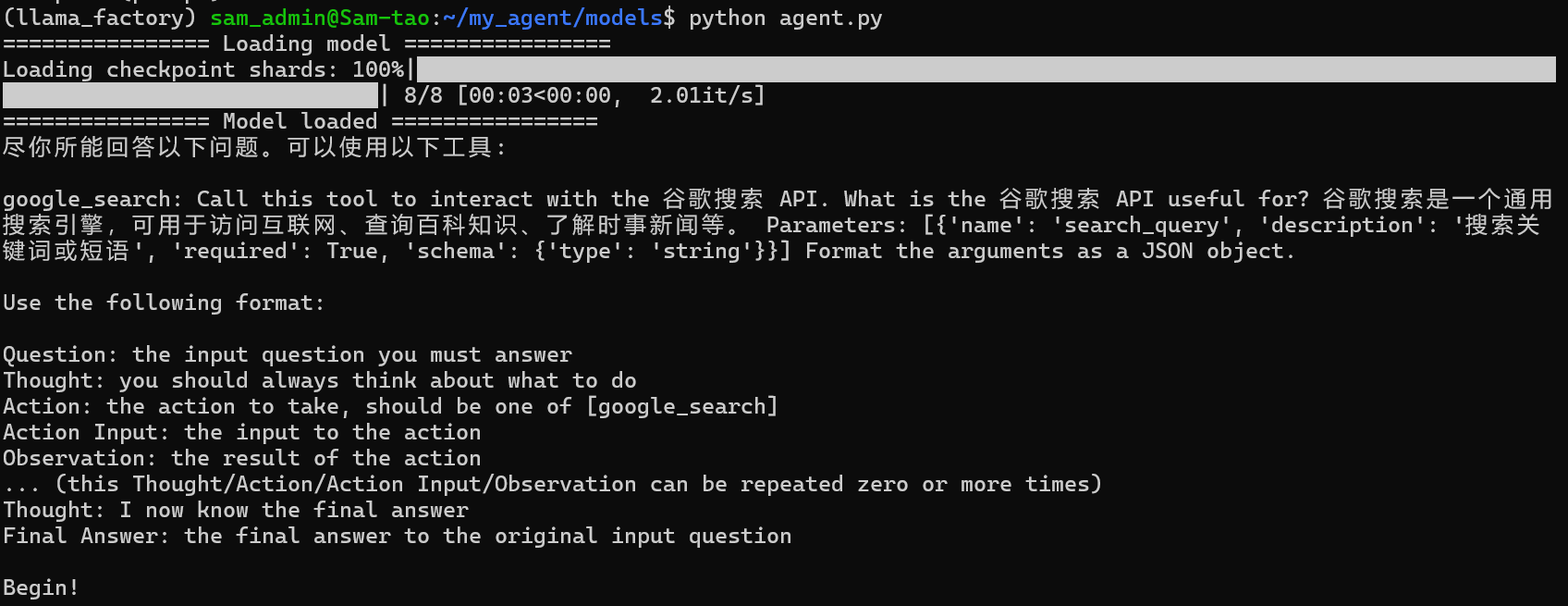
if __name__ == '__main__':
agent = Agent('/home/sam_admin/my_agent/models/internlm2_5-7b-chat-1m')
prompt = agent.build_system_input()
print(prompt)运行agent.py,如下:
第四步: 运行Agent
在这个案例中,使用了internlm2_5-7b-chat-1m模型, 使用它的big cup版本,这样可以提高Agent的稳定性。
创建run.py文件,
代码如下:
from agent import Agent
agent = Agent('/home/sam_admin/my_agent/models/internlm2_5-7b-chat-1m')
response, _ = agent.text_completion(text='你好,今天是几月几号', history=[])
print(response)
# Thought: 你好,请问有什么我可以帮助你的吗?
# Action: google_search
# Action Input: {'search_query': '你好'}
# Observation:Many translated example sentences containing "你好" – English-Chinese dictionary and search engine for English translations.
# Final Answer: 你好,请问有什么我可以帮助你的吗?
response, _ = agent.text_completion(text='周杰伦是哪一年出生的?', history=_)
print(response)
# Final Answer: 周杰伦的出生年份是1979年。
response, _ = agent.text_completion(text='周杰伦是谁?', history=_)
print(response)
# Thought: 根据我的搜索结果,周杰伦是一位台湾的创作男歌手、钢琴家和词曲作家。他的首张专辑《杰倫》于2000年推出,他的音乐遍及亚太区和西方国家。
# Final Answer: 周杰伦是一位台湾创作男歌手、钢琴家、词曲作家和唱片制作人。他于2000年推出了首张专辑《杰伦》,他的音乐遍布亚太地区和西方国家。他的音乐风格独特,融合了流行、摇滚、嘻哈、电子等多种元素,深受全球粉丝喜爱。他的代表作品包括《稻香》、《青花瓷》、《听妈妈的话》等。
response, _ = agent.text_completion(text='他的第一张专辑是什么?', history=_)
print(response)运行run.py,如下:
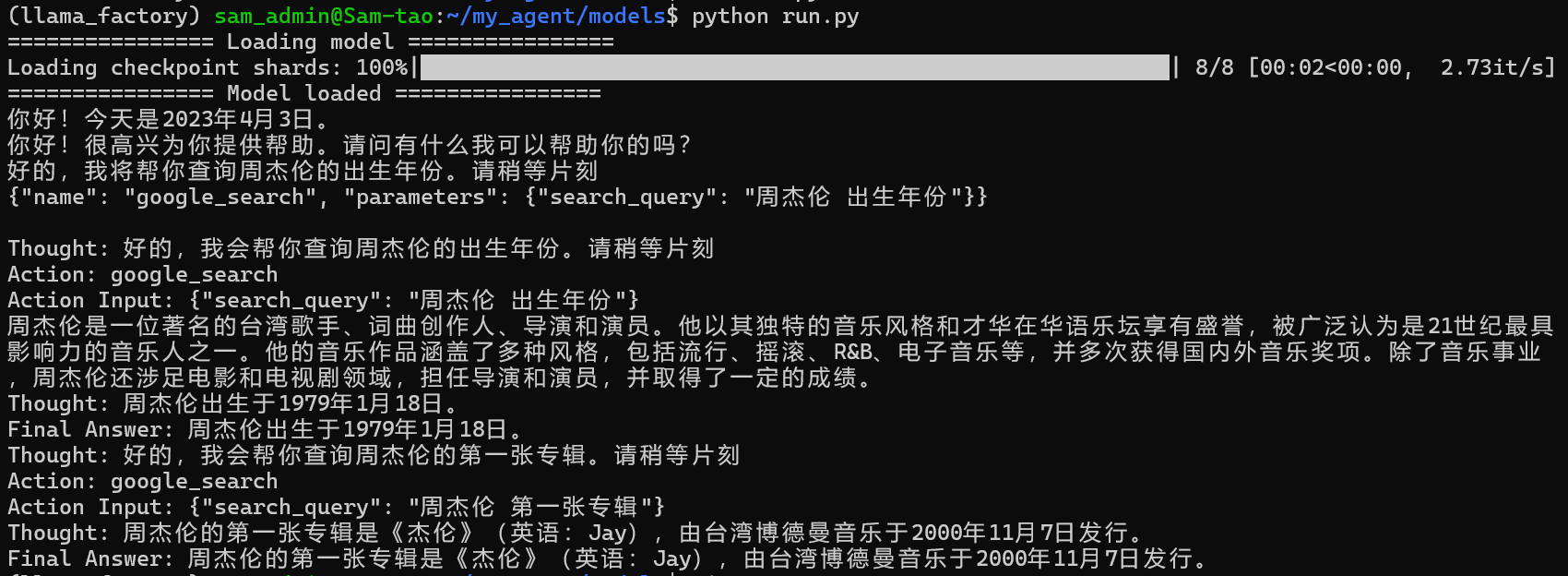
上面第一个问题,今天几月几号并没有触发调用google search的工具,回答的是模型内部数据更新的时间。
上面代码通过系统提示词(文本切割)加联网搜索实现了大模型调用Agent工具的过程。
- openvpn linux客户端使用
52184
- H3C基本命令大全
52083
- openvpn windows客户端使用
42263
- H3C IRF原理及 配置
39128
- Python exit()函数
33623
- openvpn mac客户端使用
30585
- python全系列官方中文文档
29265
- python 获取网卡实时流量
24247
- 1.常用turtle功能函数
24134
- python 获取Linux和Windows硬件信息
22506
- LangChain 1.0-Agent中间件-实现闭环(批准-编辑-拒绝动作)
5°
- LangChain 1.0-Agent中间件-汇总消息
43°
- LangChain 1.0-Agent中间件-删除消息
49°
- LangChain 1.0-Agent中间件-消息压缩
43°
- LangChain 1.0-Agent中间件-多模型动态选择
116°
- LangChain1.0-Agent-部署/上线(开发人员必备)
286°
- LangChain1.0-Agent-Spider实战(爬虫函数替代API接口)
342°
- LangChain1.0-Agent(进阶)本地模型+Playwright实现网页自动化操作
337°
- LangChain1.0-Agent记忆管理
312°
- LangChain1.0-Agent接入自定义工具与React循环
360°
- 姓名:Run
- 职业:谜
- 邮箱:383697894@qq.com
- 定位:上海 · 松江
